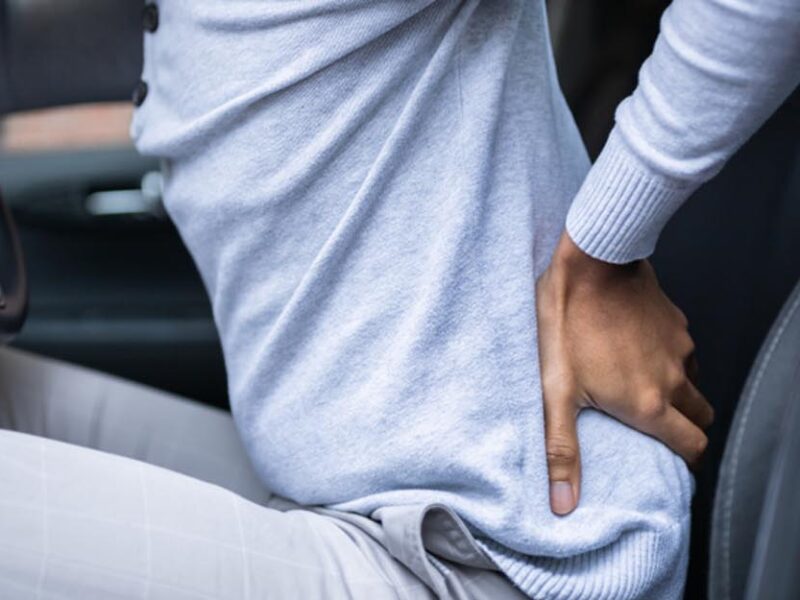
Backache, a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide, manifests as discomfort or pain in the region of the back. It encompasses a wide spectrum of causes, ranging from sedentary lifestyles to serious medical conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of backache, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Backache
The back, a complex structure comprising bones, muscles, ligaments, and nerves, provides stability, support, and flexibility to the body. Backache can originate from various structures within this intricate framework.
Common causes include muscle strains, ligament sprains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as poor posture, obesity, lack of exercise, and heavy lifting contribute significantly to the development of backache.
Symptoms
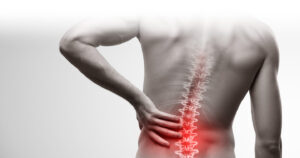
The symptoms of backache vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common manifestations include localized or radiating pain, stiffness, muscle spasms, tingling sensations, and weakness in the back or legs. The intensity of pain can range from mild discomfort to debilitating agony, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life and functional abilities.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis forms the cornerstone of effective management of backache. Healthcare professionals employ a multifaceted approach, incorporating detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, CT scans, and nerve studies to identify the underlying cause of back pain and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment
Treatment strategies for backache encompass a multimodal approach aimed at alleviating pain, promoting healing, restoring function, and preventing recurrence. Conservative measures include rest, ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain medications, physical therapy, and chiropractic care.
In cases of severe or persistent pain, interventions such as epidural steroid injections, nerve blocks, or surgical procedures may be considered to address specific structural abnormalities or pathology.
Prevention
Prevention plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of developing backache and maintaining spinal health. Adopting ergonomic principles, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen core muscles, practising good posture, using proper lifting techniques, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing are fundamental preventive measures.
Moreover, fostering a balanced lifestyle that prioritizes physical activity, stress management, and adequate rest contributes to overall well-being and reduces the likelihood of backache.
Alternative Therapies
In recent years, alternative therapies have gained popularity as adjunctive treatments for backache. These include acupuncture, massage therapy, yoga, tai chi, and herbal supplements. While evidence supporting their efficacy varies, many individuals find relief from back pain through these holistic approaches, either independently or in combination with conventional medical interventions.
Psychosocial Factors
It is essential to recognize the influence of psychosocial factors on the experience of backache. Chronic pain can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and impaired social functioning.
Addressing these psychosocial aspects through cognitive-behavioural therapy, relaxation techniques, mindfulness-based stress reduction, and support groups can enhance coping mechanisms and improve overall outcomes in individuals with backache.
Conclusion
Backache represents a multifaceted and pervasive health concern with diverse underlying causes and manifestations.
By understanding its complexities and adopting a comprehensive approach to management encompassing diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and psychosocial support, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges posed by back pain, reclaiming comfort, mobility, and vitality in their lives.
Through collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, patients, and communities, we can strive towards a future where backache is not a barrier but a manageable aspect of human health and well-being.
Related Tags
Taiwo Olawuyi
Taiwo Olawuyi is a highly dedicated and passionate professional blogger, renowned for her ability to create captivating, informative, and engaging content in the realm of health and wellness. She holds a Bachelor's degree in Political Science from Olabisi Onabanjo University and a Master's degree in Adult Education from the prestigious University of Ibadan. Her profound passion for health and wellness, coupled with her unwavering dedication to her audience, serves as a constant source of inspiration and enlightenment for readers worldwide.