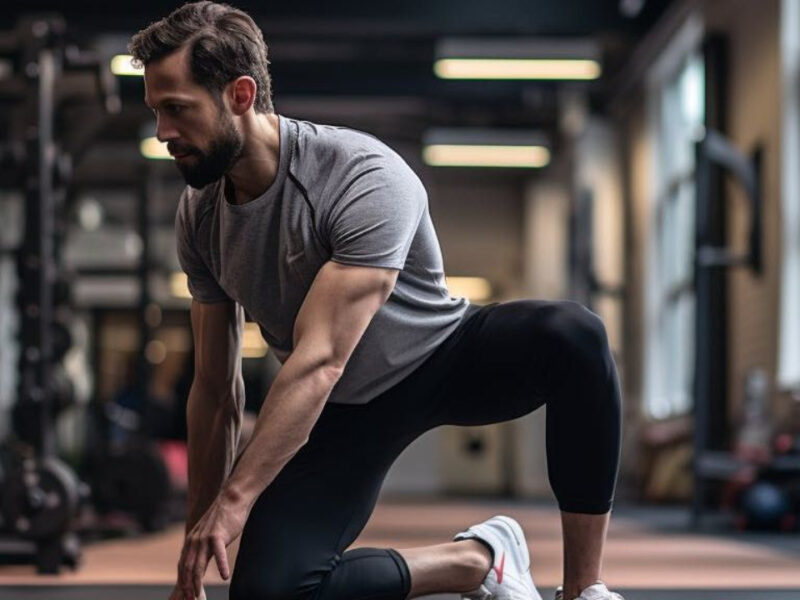
Introduction: Functional fitness has emerged as a popular trend in the fitness industry, offering a holistic approach to training that focuses on improving movement patterns and enhancing everyday functionality. Unlike traditional gym workouts that often isolate muscle groups, functional training emphasizes movements that mimic real-life activities, making it more relevant and practical for daily life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the rise of functional fitness and how it’s reshaping workouts for individuals of all fitness levels.
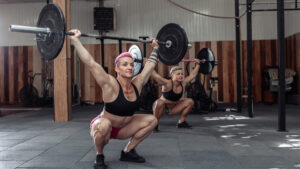
- Understanding Functional Fitness:
- Functional fitness is a training approach that emphasizes movements that closely mimic activities of daily living, such as squatting, bending, lifting, pushing, and pulling.
- The goal of functional training is to improve overall movement quality, stability, balance, coordination, and strength to enhance performance in everyday activities and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Core Principles of Functional Training:
- Core stability and strength are fundamental to functional fitness, as the core serves as the foundation for all movement.
- Functional exercises often involve multi-joint movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, rather than isolating individual muscles.
- Movements are performed in various planes of motion, including sagittal (forward and backward), frontal (side-to-side), and transverse (rotational), to improve overall movement proficiency and functionality.
- Benefits of Functional Fitness:
- Improved Movement Quality: Functional training focuses on movement patterns rather than isolated muscles, leading to more efficient and effective movement mechanics.
- Enhanced Functional Strength: Functional exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, improving overall strength and stability in everyday activities.
- Injury Prevention: By improving movement quality, stability, and balance, functional training can help reduce the risk of injuries both in and out of the gym.
- Increased Core Stability: Core-focused exercises in functional training help strengthen the muscles of the core, improving posture and reducing the risk of back pain and injury.
- Greater Functional Capacity: Functional fitness improves overall physical capacity and performance in activities of daily living, such as lifting groceries, climbing stairs, or playing with children.
- Common Functional Exercises:
- Squats: Functional squats involve squatting down as if sitting in a chair, engaging the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps while maintaining proper alignment of the spine and hips.
- Lunges: Lunges target the lower body muscles, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, while improving balance and stability.
- Push-ups: Push-ups strengthen the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core muscles while promoting proper alignment and stability throughout the body.
- Rows: Rowing exercises target the muscles of the upper back, shoulders, and arms, improving posture and upper body strength.
- Dead-lifts: Dead-lifts engage the muscles of the lower back, glutes, hamstrings, and core, promoting hip hinge mechanics and proper lifting technique.
- Integrating Functional Training Into Workouts:
- Incorporate functional exercises into your existing workout routine by replacing traditional exercises with functional alternatives.
- Focus on performing movements with proper form and technique, emphasizing quality over quantity.
- Use a variety of equipment, such as kettlebells, dumbbells, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises, to add variety and challenge to your workouts.
- Incorporate functional movements into circuit training, interval training, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts for a comprehensive and effective training session.
- Progressing in Functional Training:
- Start with basic functional exercises and gradually progress to more advanced variations as your strength, stability, and coordination improve.
- Focus on mastering movement patterns and maintaining proper form before increasing resistance or intensity.
- Incorporate balance and stability exercises, such as single-leg squats, stability ball exercises, and balance board exercises, to further challenge your functional fitness.
- Listening to Your Body:
- Pay attention to how your body feels during functional training workouts and adjust exercises or intensity as needed.
- Avoid pushing through pain or discomfort and prioritize proper form and technique to prevent injuries.
- Seeking Professional Guidance:
- Work with a certified personal trainer or fitness professional who specializes in functional training to develop a personalized workout program tailored to your individual needs and goals.
- A knowledgeable trainer can provide guidance on exercise selection, technique, progression, and modification to ensure safe and effective workouts.
Conclusion: Functional fitness offers a practical and effective approach to training that focuses on improving movement quality, functionality, and performance in everyday activities. By incorporating functional exercises into your workout routine and focusing on movement patterns rather than isolated muscles, you can enhance strength, stability, balance, and overall fitness while reducing the risk of injuries. Whether you’re new to fitness or a seasoned athlete, functional training can help you achieve your goals and live a healthier, more functional life.