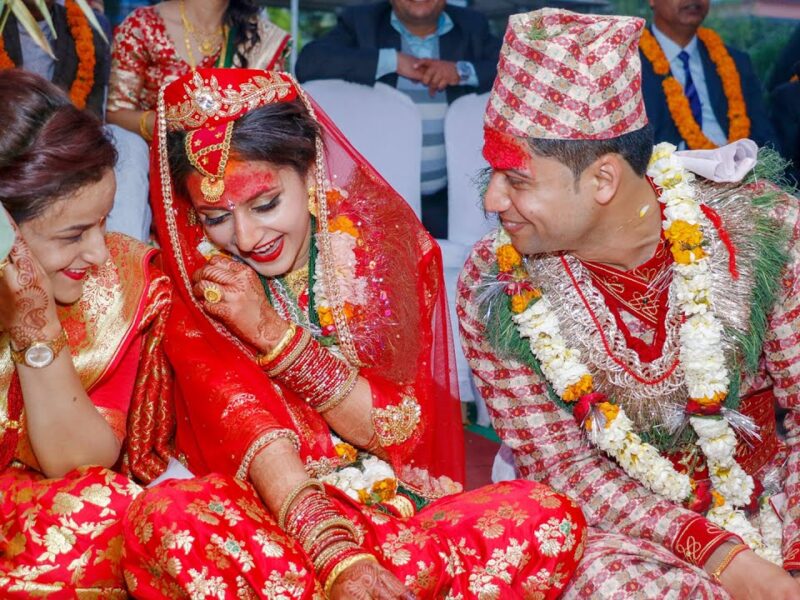
Nepal, nestled in the heart of the Himalayas, is renowned for its stunning landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and diverse ethnic groups. Among the many intriguing aspects of Nepalese culture is the practice of polyandry, particularly prevalent among the Sherpa people residing in the remote mountainous regions.
This essay delves into the unique dynamics of polyandry in Nepal, focusing on its prevalence among the Sherpa community, the socio-economic factors driving this practice, and its cultural significance in shaping familial and landholding structures.
Polyandry Among the Sherpa People
Polyandry, the practice of one woman having multiple husbands, is a longstanding tradition among the Sherpa people of Nepal. This practice is deeply ingrained in Sherpa culture and has been passed down through generations, shaping familial relationships and community dynamics.
Geographic Context
The mountainous terrain of the Himalayas, where the Sherpa people reside, plays a significant role in the prevalence of polyandry. In these remote regions, where land is scarce and agriculture is challenging, polyandry offers practical advantages for households by pooling resources and reducing the fragmentation of landholdings.
Economic Considerations
Economic factors heavily influence the practice of polyandry among the Sherpa people. Polyandrous households can maximise agricultural productivity by consolidating resources and labour in mountainous areas with limited arable land. Additionally, polyandry helps mitigate the challenges of land inheritance, ensuring that family property remains intact and accessible to all members.
Resource Sharing and Cooperation
Polyandrous households in Nepal operate on principles of cooperation and mutual support. By sharing responsibilities for household chores, childcare, and agricultural work, multiple husbands can alleviate the burdens placed on individual spouses. This collaborative approach fosters strong bonds within the family unit and promotes resilience in adversity.
Cultural Significance

Polyandry holds profound cultural significance among the Sherpa people, reflecting values of communalism, reciprocity, and resilience. This practice is deeply intertwined with religious beliefs, social norms, and customary laws that govern family life and community relations. Polyandrous unions are celebrated as symbols of unity, strength, and continuity within Sherpa society.
Challenges and Adaptations
While polyandry offers practical benefits for Sherpa households, it also presents unique challenges and complexities. Managing interpersonal relationships, ensuring equitable treatment of spouses, and navigating societal norms require careful negotiation and communication within polyandrous families.
Moreover, modernization and external influences pose challenges to the sustainability of polyandrous practices, leading to adaptations and changes in Sherpa communities.
Contemporary Perspectives
In recent years, the prevalence of polyandry among the Sherpa people has declined due to various factors, including increased access to education, economic opportunities, and exposure to alternative lifestyles.
While polyandry remains a cherished aspect of Sherpa culture, younger generations may choose alternative family arrangements based on individual preferences and changing societal norms.
Cultural Preservation and Adaptation
As Nepal undergoes rapid socio-economic transformation, preserving traditional cultural practices like polyandry while adapting to modern realities poses a delicate balance. Efforts to safeguard Sherpa’s culture and heritage, including polyandrous traditions, are essential for maintaining cultural diversity and promoting intergenerational continuity.
Conclusion
Polyandry among the Sherpa people of Nepal offers a fascinating glimpse into the complex interplay of geography, economics, and culture in shaping familial and societal dynamics. Rooted in centuries-old traditions, polyandry reflects the resilience and resourcefulness of mountain communities grappling with the challenges of life in the Himalayas.
As Nepal continues to evolve in the 21st century, navigating the delicate balance between tradition and modernity will be crucial for preserving the cultural heritage of the Sherpa people while embracing the opportunities of a rapidly changing world.
Related Tags
Taiwo Olawuyi
Taiwo Olawuyi is a highly dedicated and passionate professional blogger, renowned for her ability to create captivating, informative, and engaging content in the realm of health and wellness. She holds a Bachelor's degree in Political Science from Olabisi Onabanjo University and a Master's degree in Adult Education from the prestigious University of Ibadan. Her profound passion for health and wellness, coupled with her unwavering dedication to her audience, serves as a constant source of inspiration and enlightenment for readers worldwide.