Muscle or ligament strain, often referred to as a “pulled muscle,” is a common cause of back pain and discomfort. This condition occurs when the muscle fibers or ligaments in the back are stretched or torn beyond their normal range of motion.
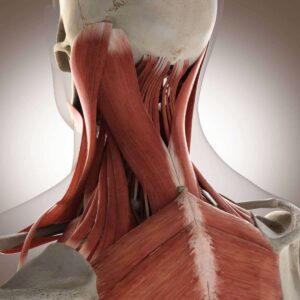
Causes
- Overexertion: Strains often result from overexertion, such as lifting heavy objects improperly or using poor lifting techniques.
- Sudden Movements: Quick, abrupt movements or twisting motions can strain back muscles and ligaments.
- Poor Posture: Maintaining poor posture, especially when sitting for extended periods, can lead to muscle imbalances and eventual strain.
- Repetitive Activities: Engaging in repetitive activities or motions that involve the back, such as heavy lifting or repetitive bending, can strain muscles and ligaments over time.
- Inactivity: Muscles and ligaments can weaken with inactivity, leaving them more susceptible to strain when sudden activity is resumed.
Symptoms
- Pain: The most common symptom of muscle or ligament strain is pain in the affected area. The pain can range from mild to severe.
- Stiffness: The affected area may become stiff and difficult to move.
- Swelling: In some cases, there may be localized swelling at the site of the strain.
- Muscle Spasms: Muscle spasms can accompany strain, leading to involuntary muscle contractions.
- Limited Range of Motion: Due to pain and stiffness, the affected individual may have difficulty moving the back or performing certain activities.
Treatment
Treatment for muscle or ligament strain typically focuses on relieving pain and promoting healing. Here are common approaches:
- Rest: Resting the affected area is crucial to allow the muscles or ligaments to heal. Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Ice and Heat: Applying ice to the affected area within the first 48 hours can help reduce pain and inflammation. After the initial phase, applying heat can help relax muscles and promote blood flow.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches to strengthen the affected muscles, improve flexibility, and prevent future strains.
- Compression: Using compression bandages or wraps can help reduce swelling and provide support to the injured area.
- Elevation: Elevating the injured area when resting can also help reduce swelling.
- Massage: Gentle massage from a trained therapist can promote blood flow and relaxation in the affected muscles.
- Gradual Return to Activity: After the initial healing period, gradually reintroduce activities and exercises to avoid re-straining the muscles or ligaments.
- Proper Posture and Body Mechanics: Learning and practicing proper posture and body mechanics can help prevent future strains.
- Medical Evaluation: In severe cases or if symptoms persist, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. They may recommend further diagnostic tests, such as imaging, and provide specialized treatments like corticosteroid injections in some cases.
Lastly, Muscle or ligament strain in the back can vary in severity, from mild discomfort that resolves with rest and self-care to more severe strains that require medical attention. Prompt and appropriate treatment can help alleviate pain, prevent complications, and promote a full recovery