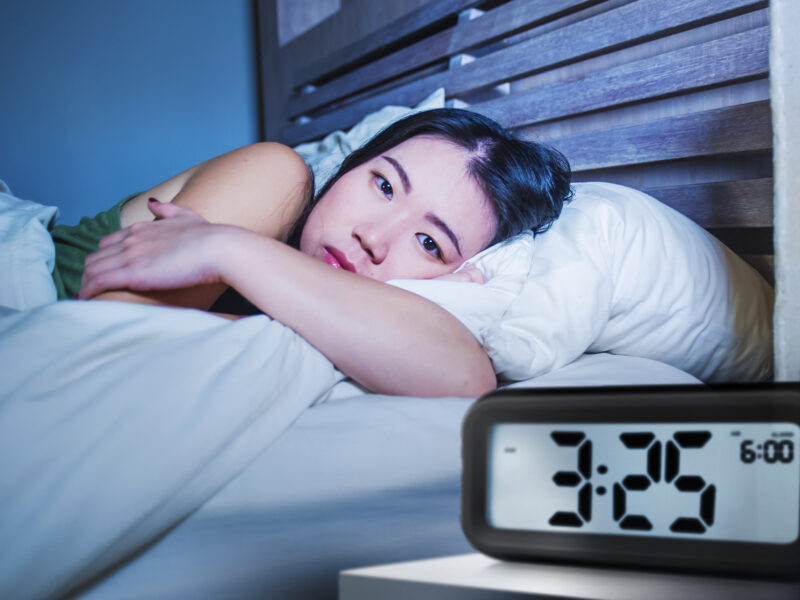
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep, despite having the opportunity and desire to sleep. It can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and other health problems.
Causes of Insomnia
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress or anxiety can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like chronic pain, allergies, asthma, acid reflux, and hormonal imbalances can disrupt sleep.
- Mental Health Disorders: Conditions such as depression and bipolar disorder can affect sleep patterns.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants, asthma medications, and stimulants, can interfere with sleep.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor sleep habits, such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, and inadequate physical activity, can contribute to insomnia.
- Environmental Factors: Noise, light, and an uncomfortable sleep environment can disrupt sleep.
Types of Insomnia
- Acute Insomnia: Short-term insomnia usually lasts for a few days or weeks and is often triggered by a specific event, such as stress or travel.
- Chronic Insomnia: Long-term insomnia persists for at least three nights a week for three months or more. It can have multiple underlying causes.

Common Symptoms of Insomnia
- Difficulty falling asleep: You may find it hard to initiate sleep when you go to bed.
- Frequent awakenings: You may wake up several times during the night and have trouble falling back asleep.
- Early morning awakening: You may wake up very early in the morning and be unable to return to sleep.
- Daytime Fatigue: Insomnia often leads to feeling tired, irritable, and having difficulty concentrating during the day.
- Mood Disturbances: Insomnia can contribute to mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of insomnia is typically based on a clinical evaluation, including a medical history, sleep history, and possibly a sleep diary. In some cases, a sleep study (polysomnography) may be recommended to rule out other sleep disorders.
Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy sleep habits, known as sleep hygiene, can help improve sleep quality. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants and heavy meals close to bedtime.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a highly effective, evidence-based therapy that focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors related to sleep. It can help individuals develop better sleep habits and address the underlying causes of insomnia.
- Medications: In some cases, short-term use of sleep medications (prescription or over-the-counter) may be recommended, but they are typically not a long-term solution due to the risk of dependency and side effects.
- Treating Underlying Conditions: If insomnia is a symptom of an underlying medical or psychiatric condition, addressing that condition may improve sleep.
- Alternative Therapies: Relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or aromatherapy, can help reduce stress and promote better sleep.
Clearly, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent insomnia, as untreated insomnia can hurt overall health and quality of life.
Treatment approaches vary depending on the underlying causes and individual circumstances, so a personalized approach is often necessary to effectively manage insomnia.