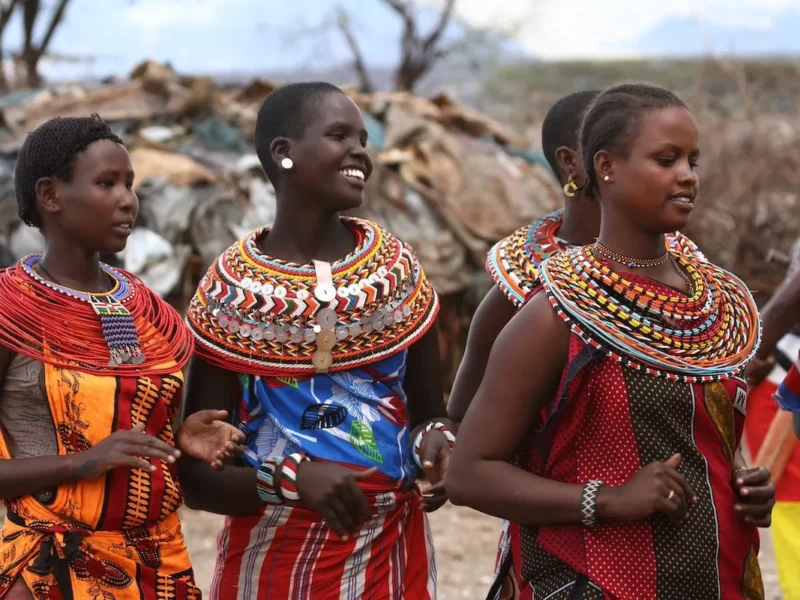
Introduction
Cultural rituals and traditions are integral aspects of human societies, encompassing a wide range of practices, beliefs, and customs passed down through generations. These rituals and traditions serve as expressions of cultural identity, social cohesion, and continuity. This note explores the significance, functions, and variations of cultural rituals and traditions, as well as the challenges and strategies for preserving them in a rapidly changing world.

The Significance of Cultural Rituals and Traditions
- Identity and Belonging: Cultural rituals and traditions are foundational to the collective identity of a community. They provide individuals with a sense of belonging and connection to their cultural heritage and community.
- Social Cohesion: Shared rituals and traditions strengthen social bonds and foster a sense of unity and solidarity among community members. They often mark important life events, seasonal changes, and religious observances.
- Transmission of Values: Through rituals and traditions, societies transmit values, beliefs, and norms to younger generations. These practices embody the moral and ethical frameworks of a culture, guiding behavior and social interactions.
- Spiritual and Emotional Fulfillment: Many rituals and traditions have spiritual or religious significance, offering individuals a sense of purpose, comfort, and continuity. They provide opportunities for reflection, celebration, and communal support.
Functions of Cultural Rituals and Traditions
- Life Cycle Events: Rituals and traditions often accompany key life cycle events, such as births, coming-of-age ceremonies, weddings, and funerals. These practices help individuals and communities navigate transitions and honor significant milestones.
- Seasonal Celebrations: Many cultures have traditions linked to seasonal changes, such as harvest festivals, solstice celebrations, and New Year festivities. These events often involve communal gatherings, feasting, and ceremonial activities.
- Religious Observances: Religious rituals and traditions play a central role in the spiritual lives of individuals and communities. They include practices like prayer, fasting, pilgrimage, and rites of passage that reinforce religious beliefs and practices.
- Cultural Expressions: Rituals and traditions encompass various forms of cultural expression, including music, dance, storytelling, and art. These practices celebrate cultural heritage and creativity, preserving and revitalizing cultural knowledge.
Variations in Cultural Rituals and Traditions
- Regional and Ethnic Differences: Cultural rituals and traditions vary widely across regions and ethnic groups, reflecting the diversity of human experiences. Each community has its unique set of practices that define its cultural identity.
- Adaptation and Innovation: While cultural rituals and traditions are rooted in history, they are not static. Communities adapt and innovate practices in response to changing social, economic, and environmental conditions.
- Intercultural Influences: Globalization and intercultural exchanges have led to the blending and borrowing of rituals and traditions across cultures. This process can enrich cultural practices but also poses challenges to authenticity and preservation.
Challenges to Preserving Cultural Rituals and Traditions
- Modernization and Urbanization: Rapid modernization and urbanization can disrupt traditional ways of life, leading to the erosion of cultural practices. As communities migrate and urbanize, maintaining traditional rituals and customs becomes more challenging.
- Globalization and Cultural Homogenization: The spread of global culture through media, technology, and economic integration can overshadow local traditions and lead to cultural homogenization. This can result in the loss of unique cultural identities.
- Economic Pressures: Economic pressures and changes in livelihoods can impact the sustainability of traditional practices. Communities may prioritize economic survival over the continuation of rituals and traditions, especially if these practices are resource intensive.
- Generational Gaps: Younger generations may be less interested in or disconnected from traditional rituals and practices. Ensuring the transmission of cultural knowledge and values requires engaging and educating youth.
Strategies for Preserving Cultural Rituals and Traditions
- Documentation and Research: Systematic documentation and research of cultural rituals and traditions are crucial for preservation. Recording practices, stories, and meanings helps safeguard intangible cultural heritage.
- Community Engagement: Involving community members in preservation efforts ensures that practices remain relevant and meaningful. Community-driven initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for cultural heritage.
- Education and Awareness: Educational programs that teach about cultural rituals and traditions can raise awareness and appreciation among younger generations. Integrating cultural heritage into school curricula and public outreach can support transmission.
- Supportive Policies and Legislation: Governments and cultural organizations can play a vital role in preserving cultural heritage through supportive policies and legislation. Protecting cultural sites, funding cultural initiatives, and recognizing intangible heritage are key actions.
- Revitalization Programs: Revitalization programs aim to breathe new life into endangered rituals and traditions. This can include festivals, workshops, and cultural exchanges that celebrate and practice traditional customs.
- Intergenerational Knowledge Transfer: Facilitating intergenerational dialogue and knowledge transfer is essential for preserving cultural heritage. Elders and cultural bearers can share their wisdom and experiences with younger community members.
Conclusion
Cultural rituals and traditions are vital for the identity, cohesion, and continuity of human societies. They embody the values, beliefs, and practices that define a community’s way of life. While challenges such as modernization, globalization, and economic pressures threaten the preservation of these cultural practices, concerted efforts in documentation, community engagement, education, and policy support can ensure their survival. By valuing and safeguarding cultural rituals and traditions, we honor the richness of human diversity and strengthen the social fabric of our communities.