Introduction
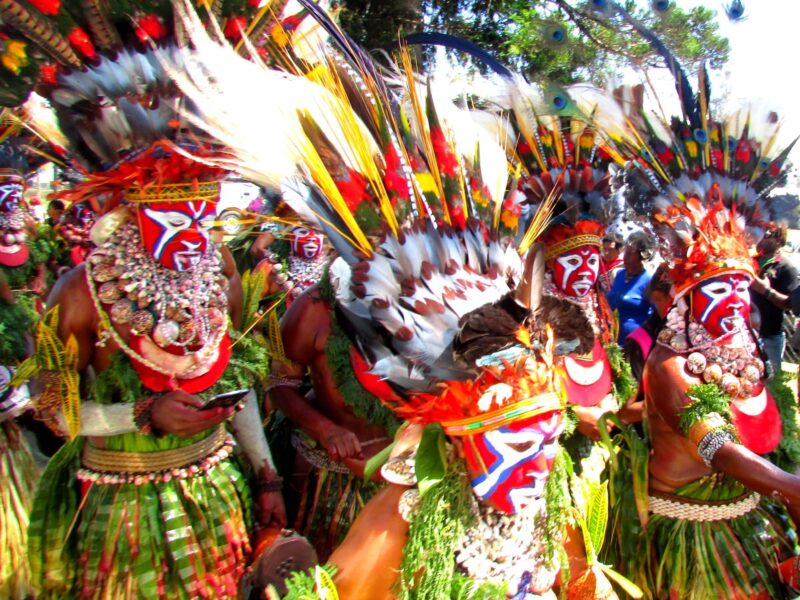
Cultural identity is a critical aspect of an individual’s self-conception and personal development. It refers to the sense of belonging to a particular cultural group and involves aspects such as nationality, ethnicity, language, and traditions. Cultural identity influences how individuals perceive themselves and are perceived by others. This note explores the interplay between cultural identity and personal development, highlighting the significance of culture in shaping personality, values, and life choices.

The Foundations of Cultural Identity
Cultural identity is formed through a combination of factors, including:
- Family and Upbringing: The family is often the primary source of cultural education. From a young age, individuals learn the language, customs, and values of their cultural group from family members. This early exposure lays the groundwork for their cultural identity.
- Language and Communication: Language is a key component of cultural identity. It not only facilitates communication but also shapes thought processes and worldviews. Multilingual individuals often navigate multiple cultural identities.
- Traditions and Rituals: Cultural traditions and rituals play a significant role in fostering a sense of belonging. Celebrations, religious practices, and communal activities reinforce cultural norms and values.
- Education and Socialization: Schools and community groups contribute to cultural identity by promoting cultural knowledge and social norms. Peer interactions and societal expectations further shape an individual’s cultural perspective.
Cultural Identity and Personal Values
Personal values are deeply influenced by cultural identity. Cultural norms dictate what is considered right or wrong, shaping moral frameworks and ethical beliefs. For instance:
- Collectivist vs. Individualist Cultures: In collectivist cultures, such as those in many Asian and African countries, individuals are taught to prioritize the needs of the group over personal desires. This fosters values like cooperation, family loyalty, and social harmony. In contrast, individualist cultures, common in Western countries, emphasize personal freedom, self-expression, and independence.
- Role of Religion: Religion often forms a core part of cultural identity, providing a moral compass and guiding life choices. Religious beliefs can influence attitudes towards various aspects of life, including marriage, work, and social responsibilities.
Cultural Identity and Self-Esteem
A strong cultural identity can enhance self-esteem and psychological well-being. Individuals who have a clear understanding of and pride in their cultural background tend to have higher self-confidence and resilience. This is because cultural identity provides a sense of purpose and belonging, which are essential for mental health.
- Positive Reinforcement: Engaging in cultural practices and receiving positive reinforcement from one’s cultural community can bolster self-worth. For example, participating in cultural festivals or being recognized for contributions to the community can reinforce a positive self-image.
- Coping Mechanism: Cultural identity can also serve as a coping mechanism during times of stress or adversity. Turning to cultural traditions and community support can provide comfort and a sense of stability.
Challenges in Cultural Identity Development
Despite its benefits, developing a strong cultural identity can be challenging, especially in multicultural or immigrant contexts.
- Acculturation Stress: Immigrants and their descendants often face acculturation stress, struggling to balance their heritage culture with the dominant culture of their new environment. This can lead to identity confusion and psychological distress.
- Discrimination and Prejudice: Experiencing discrimination based on cultural background can negatively impact self-esteem and hinder the development of a positive cultural identity. It can also create internal conflicts about cultural affiliation.
- Cultural Assimilation: In some cases, the pressure to assimilate into the dominant culture can lead individuals to downplay or abandon their cultural heritage, resulting in a loss of cultural identity and a weakened sense of self.
Strategies for Promoting Healthy Cultural Identity Development
To support the healthy development of cultural identity and personal growth, several strategies can be employed:
- Cultural Education: Providing comprehensive cultural education that includes history, language, and traditions can help individuals understand and appreciate their cultural heritage.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging participation in cultural community activities can strengthen cultural ties and provide a supportive network.
- Inclusive Policies: Promoting inclusive policies in schools, workplaces, and public spaces can reduce discrimination and foster a sense of belonging for individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Intercultural Dialogue: Facilitating intercultural dialogue and exchange can promote mutual understanding and respect among different cultural groups. This can help individuals appreciate both their own and others’ cultural identities.
- Psychological Support: Providing psychological support for individuals facing identity crises or acculturation stress can help them navigate these challenges and develop a strong, positive cultural identity.
Conclusion
Cultural identity is a foundational element of personal development, influencing values, self-esteem, and life choices. While it can present challenges, especially in multicultural contexts, fostering a strong and positive cultural identity is crucial for psychological well-being and social cohesion. By promoting cultural education, community engagement, and inclusive practices, societies can support individuals in developing a robust cultural identity that enriches their personal and collective lives.