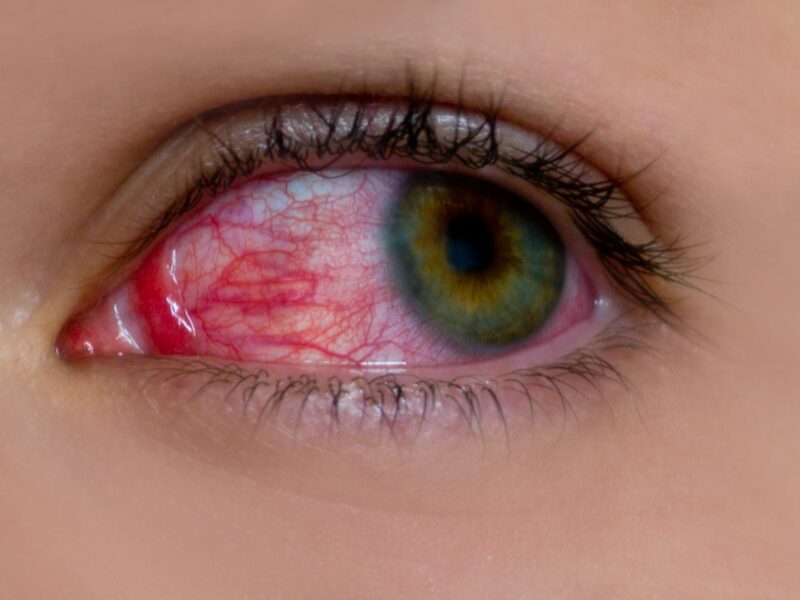
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is the inflammation of the conjunctiva (the thin) clear tissue covering the white part of the eye and lining the inside of the eyelids. This condition can be caused by various factors, including infections, allergies, and irritants. Conjunctivitis is highly contagious, and it can affect one or both eyes.
Types of Conjunctivitis
- Infectious Conjunctivitis: Caused by bacteria or viruses, and it can be highly contagious.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Often characterized by a yellow or greenish discharge.
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Commonly associated with upper respiratory infections and may cause watery discharge.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Triggered by allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander. It’s not contagious.
- Irritant Conjunctivitis: Caused by irritants like smoke, chemicals, or foreign bodies. It’s not infectious.

Symptoms
- Redness: The whites of the eyes may appear pink or red.
- Watery Eyes: Excessive tearing is common.
- Discharge: Depending on the cause, there may be a watery, mucous, or purulent discharge.
- Itchiness and Irritation: Eyes may feel itchy or irritated.
- Swelling: Swelling of the conjunctiva may occur.
Causes
- Infections: Bacterial and viral infections, such as those causing colds or respiratory illnesses.
- Allergies: Reaction to allergens like pollen, mold, dust, or pet dander.
- Irritants: Exposure to smoke, pollution, chemicals, or foreign objects.
- Contact Lenses: Improper lens care or extended wear can contribute.
Transmission
- Person-to-Person: Infectious conjunctivitis is highly contagious and can spread through contact with contaminated hands, surfaces, or personal items.
- Airborne Allergens: Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and results from exposure to allergens in the environment.
Diagnosis
- Clinical Examination: Healthcare professionals can often diagnose conjunctivitis based on symptoms and an eye examination.
- Laboratory Tests: In some cases, swabs or other tests may be done to determine the specific cause, especially for bacterial or viral infections.
Treatment
- Infectious Conjunctivitis:
- Bacterial: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be prescribed.
- Viral: Antiviral medications may be used, but viral conjunctivitis often resolves on its own.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis:
- Antihistamine eye drops or oral medications can help manage symptoms.
- Avoidance of allergens is recommended.
- Irritant Conjunctivitis:
- Removing or avoiding the irritant is the primary treatment.
Self-Care and Prevention
- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Frequent handwashing helps prevent the spread of infectious conjunctivitis.
- Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
- Avoidance of Allergens:
- Individuals with allergic conjunctivitis should identify and minimize exposure to triggers.
- Contact Lens Care:
- Proper cleaning and care of contact lenses can reduce the risk of irritant or infectious conjunctivitis.
Complications
- Corneal Involvement: Severe or untreated cases may lead to corneal complications.
- Chronic Conjunctivitis: Long-term inflammation may occur in some cases.
Special Considerations for Children
- School Settings: Because infectious conjunctivitis is highly contagious, affected children may need to stay home until the infection is no longer spreading.
- Eye Care: Teaching children proper eye hygiene is essential.
Seasonal and Environmental Factors
- Seasonal Allergies: Allergic conjunctivitis may be more prevalent during certain seasons with high pollen counts.
- Environmental Conditions: Pollution, smoke, or dry air can contribute to irritant conjunctivitis.
Professional Advice:
- Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Global Impact:
- Conjunctivitis affects people worldwide and can be a common reason for seeking medical care.
In summary, conjunctivitis is a common condition that can result from infections, allergies, or irritants. It manifests with redness, discharge, and discomfort; the appropriate treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Practicing good hygiene, avoiding allergens or irritants, and seeking timely medical attention contribute to effective management and prevention of complications.
Related Tags
Taiwo Olawuyi
Taiwo Olawuyi is a highly dedicated and passionate professional blogger, renowned for her ability to create captivating, informative, and engaging content in the realm of health and wellness. She holds a Bachelor's degree in Political Science from Olabisi Onabanjo University and a Master's degree in Adult Education from the prestigious University of Ibadan. Her profound passion for health and wellness, coupled with her unwavering dedication to her audience, serves as a constant source of inspiration and enlightenment for readers worldwide.