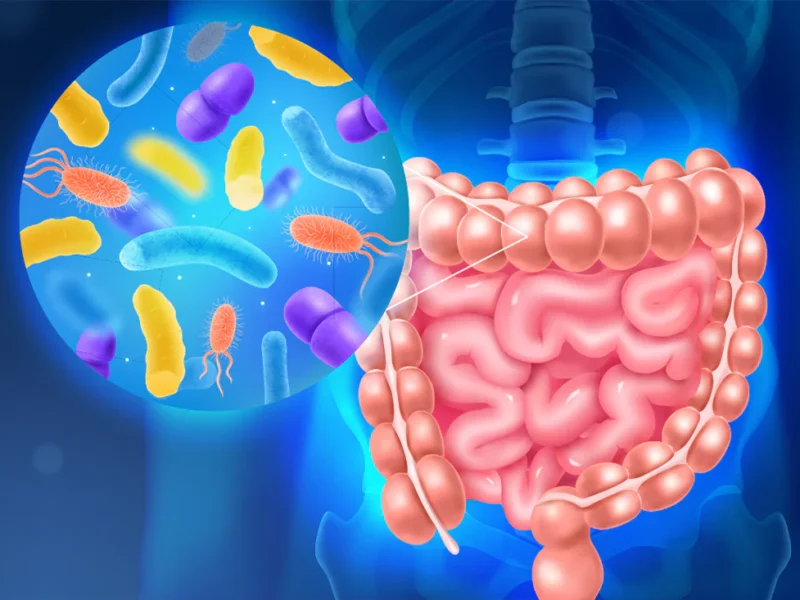
The human body is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiome, which play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. These microorganisms, primarily residing in our gastrointestinal tract, influence various bodily functions, from digestion and immune response to mental health and metabolism. This exploration delves into the intricacies of the microbiome and its profound impact on our well-being.

Understanding the Microbiome
The microbiome encompasses a diverse community of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that inhabit different parts of our body, with the majority located in the intestines. This microbial ecosystem is unique to each individual, shaped by factors such as genetics, diet, environment, and lifestyle. The balance and diversity of these microorganisms are essential for optimal health.
The Role of the Microbiome in Digestion
One of the primary functions of the gut microbiome is aiding in the digestion of complex carbohydrates, fibers, and proteins that our bodies cannot process independently. These microbes break down these substances, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate, which serve as energy sources for colon cells and have anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, the microbiome synthesizes essential vitamins and nutrients, including vitamin K and certain B vitamins, crucial for metabolic processes and overall health.
Immune Function and the Microbiome
The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in regulating the immune system. It acts as a protective barrier, preventing harmful pathogens from colonizing the intestines. The microbiome also communicates with immune cells, training and modulating the immune response to ensure it effectively combats infections while avoiding unnecessary inflammation. A balanced microbiome contributes to a robust immune system, whereas an imbalance, known as dysbiosis, can lead to immune dysregulation and increase the risk of infections, allergies, and autoimmune diseases.
The Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, significantly influenced by the microbiome. This connection involves the vagus nerve, the immune system, and microbial metabolites. Certain gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for mood regulation. Dysbiosis has been linked to mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and neurodevelopmental disorders like autism, highlighting the importance of a healthy microbiome for mental well-being.
Metabolic Health and the Microbiome
The microbiome significantly impacts metabolic health, influencing weight management and the risk of metabolic disorders. Research shows that individuals with a diverse and balanced gut microbiome tend to have a healthier metabolism and lower body fat levels. Certain gut bacteria regulate appetite, energy extraction from food, and fat storage. Dysbiosis can disrupt these processes, leading to metabolic imbalances and an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic diseases. Diet plays a crucial role in shaping the microbiome, with fiber-rich foods promoting microbial diversity and metabolic health.
The Microbiome and Chronic Diseases
The microbiome’s influence extends to various chronic diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), cardiovascular disease, cancer, and autoimmune conditions. For example, in IBD, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the balance of gut bacteria is disrupted, leading to chronic inflammation and intestinal damage. Restoring a healthy microbiome through dietary interventions, probiotics, and prebiotics has shown promise in managing these conditions. Similarly, the microbiome can influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation, affecting cardiovascular health. Research also suggests that the microbiome can impact cancer treatment efficacy and modulate inflammation, a critical factor in cancer development and progression.
Maintaining a Healthy Microbiome
Maintaining a balanced and diverse microbiome is essential for overall health. Here are some strategies to support a healthy microbiome:
- Eat a Diverse Diet: Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods provides the nutrients and fibers that support microbial diversity and health.
- Include Probiotics and Prebiotics: Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods and supplements, while prebiotics are fibers that feed these bacteria. Both are essential for a healthy microbiome.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: Processed foods and high sugar intake can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and promote the growth of harmful microbes.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports overall digestive health and the function of the gut microbiome.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity positively influences the composition of the gut microbiome.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular relaxation can help maintain a healthy gut.
- Use Antibiotics Sparingly: While antibiotics are necessary for treating bacterial infections, their overuse can disrupt the microbiome. Only use antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow their guidance on probiotic use during and after antibiotic treatment.
The Future of Microbiome Research
The study of the microbiome is an evolving field, with ongoing research aimed at uncovering more specific microbial functions and their impact on various health conditions. Future advancements in microbiome research hold the potential for personalized medicine, where treatments and dietary recommendations can be tailored to an individual’s unique microbiome composition. This personalized approach could revolutionize healthcare, offering more effective and targeted interventions for maintaining health and preventing disease.
Conclusion
The microbiome is a powerful and dynamic component of our biology, intricately linked to numerous aspects of our health. From digestion and immunity to mental well-being and metabolic health, the influence of our microbial communities is vast and profound. By understanding and nurturing our microbiome through diet, lifestyle, and mindful choices, we can harness its potential to promote overall health and well-being. As research continues to unfold, the promise of the microbiome in transforming healthcare becomes increasingly evident, highlighting the importance of this “gut feeling” in our pursuit of optimal health.