Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the lungs, usually in the cells lining air passages. It is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally.
It can be broadly categorized into two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention measures is crucial for addressing lung cancer.
Risk Factors
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is the primary cause of lung cancer, responsible for a majority of cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk.
- Occupational Exposures: Asbestos, radon, certain metals, and other workplace exposures can contribute.
- Family History: A family history of lung cancer may increase the risk.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to high levels of air pollution may be a risk factor.
Types of Lung Cancer
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This is the most common type, comprising about 85% of cases. Subtypes include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This type is less common but tends to grow and spread more rapidly.
Symptoms
- Symptoms may not appear in the early stages.
- Common symptoms include persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, weight loss, and recurrent respiratory infections.
Diagnosis
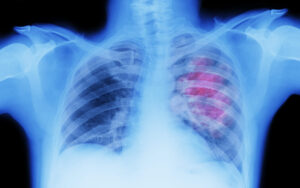
- Imaging Studies: Chest X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans can detect abnormalities in the lungs.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples are taken for examination under a microscope to confirm cancer and determine its type.
Staging
- Lung cancer is staged from I to IV, with higher stages indicating more advanced disease.
- Staging helps determine the extent of cancer spread and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
- Surgery: Removing the tumor or affected lung tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapies: Drugs targeting specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Survival Rates
- Survival rates vary based on the stage at diagnosis and the type of lung cancer.
- Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes.
Impact on Quality of Life
- Lung cancer and its treatment can affect the patient’s physical and emotional well-being.
- Supportive care, palliative care, and survivorship programs play essential roles.
Clinical Trials
- Participation in clinical trials is an option for some patients, providing access to experimental treatments and contributing to medical research.
Prevention
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer.
- Avoiding Secondhand Smoke: Minimizing exposure to secondhand smoke is important.
- Radon Testing: Testing and mitigating high levels of radon in homes can reduce the risk.
- Occupational Safety: Minimizing exposure to occupational carcinogens, such as asbestos, is crucial.
Screening Guidelines
- Low-Dose CT Scan: Some high-risk individuals, such as heavy smokers, may be recommended for regular low-dose CT scans for early detection.
Global Burden
- Lung cancer is a major public health challenge worldwide, with a high incidence and mortality rate.
- Prevention efforts, early detection, and access to effective treatments are crucial on a global scale.
Advancements in Research
- Ongoing research explores new treatments, early detection methods, and the role of genetics in lung cancer.
- Understanding the molecular basis of lung cancer has led to targeted therapies.
Public Awareness
- Public health campaigns aim to raise awareness about the risks of smoking, the importance of early detection, and the potential for prevention.
In summary, lung cancer is a complex disease with various risk factors and types. Prevention, early detection, and advancements in treatment options are critical in addressing the global impact of lung cancer.
Public awareness, research efforts, and comprehensive healthcare strategies contribute to improving outcomes and reducing the burden of this devastating disease.










1 comment
I have no doubt that this site will become famous owing to its high-quality articles as soon as its administrator starts working.